PHARMACEUTICAL VALIDATION
In order for pharmaceutical companies to be able to produce or package medicines, the competent authorities must issue an authorisation. The company can obtain the approval if it can be demonstrate that the production and packaging processes are carried out in accordance with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice). The demonstration of the use of processes that follow these criteria is achieved through the Validation activity. Validation is a formal activity that follows the entire life cycle of the processes, considering the machines, the structures, the methods, the utilities, the controls and in general everything that can cause a danger to the end user, namely the patient.
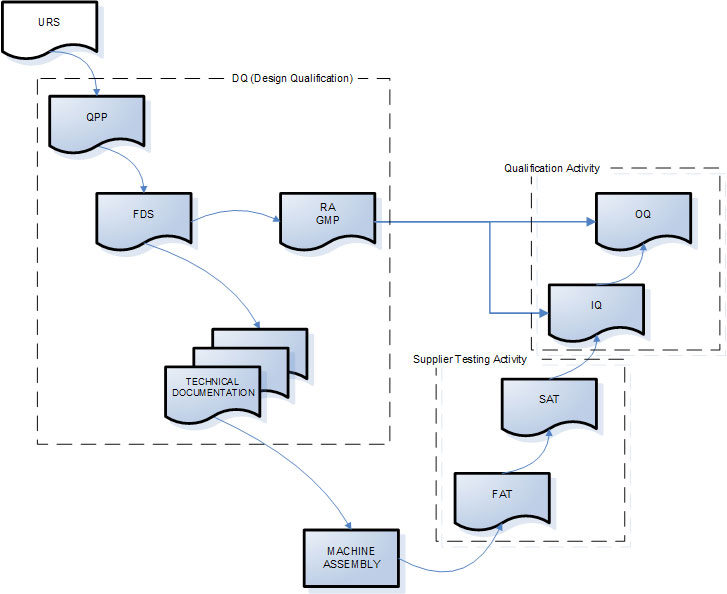
As the validation is a formal activity, it requires documented evidence of decisions taken and activities carried out. The documented evidence is made through the use of documents drawn up, verified and approved before the use by the personnel who hold responsibility in order to be able to declare their authenticity and usability.
WHAT IS IT NECESSARY TO VALIDATE?
Generally speaking, it is necessary to validate any aspect that may have an impact on a patient safety, considering that this is compromised by the loss of integrity of the critical data recorded, by the lack and/or incorrectness of information relating to the use of the medicine and in general by any aspect that weighs on the physical, chemical and therapeutic attributes of the medicine.
THE PRODUCTION AND PACKAGING PROCESS
The drugs are manufactured using manufacturing and packaging processes. Each process is defined by the following elements: